What are the different concepts related to Costs? Describes the relation between the average cost and marginal cost.
Concepts of Costs:- Costs concepts are used in a different way in economics as following:
- Money Cost
- Real Cost
- Accounting Costs
- Opportunity Costs
- Economic Costs
- Social Costs
- Private Cost
- Explicit Cost
- Implicit Cost
- Money Cost:- The Expenditure which is incurred in terms of money for the purpose of production is called Money Cost. Example :- wages paid, Taxes, Transportation Charges, Expenditure on raw materials.
- Real Cost:- The mental and physical efforts paid for producing a commodity is called real Cost. Which efforts give pain, and discomfort to the Real Owner who supplies the factor of production. It is a subjective concept.
- Accounting Cost:- Which costs are recorded in the books of accounts as depreciation and cash payments. It refers to historical costs and pocket costs.
- Opportunity Costs:- When we invest money in the form of expenditure to produce one thing, what was given up in terms of money but this money is sacrificed for next best alternatives is called Opportunity cost. Because one project is undertaken but another opportunity is foregone. It is called opportunity costs.
- Economic Costs:- Sometimes the owner supplies his own resources of production to the business otherwise his resources could earn some profit which he would have to forego. As self Employed in business for producing commodities.
- Social Costs:- Social cost is concerned with the Social cost such as Pollution and Noise. Which is borne by society like the cost, people have to bear on account of water pollution and noise pollution.
- Private Costs:- These are those costs which are borne by individual firms or individual producers as a result of their own decision making in their business operations. In short, Private costs are equal to social costs minus external costs.
- Explicit Costs:- Which sources are arranged by firms for the purpose of production, and monetary payments are made to those outsiders who supply labour services, material, fuel, transportation service, power and so on are called Explicit Costs.
- Implicit Costs:- Some inputs are self owned and self employed by the firms. The firm does not pay any payment to anyone. Rather it forgoes the opportunity to earn income from someone, Example – to whom it could sell and lease out of self owned resources is called implicit Costs.
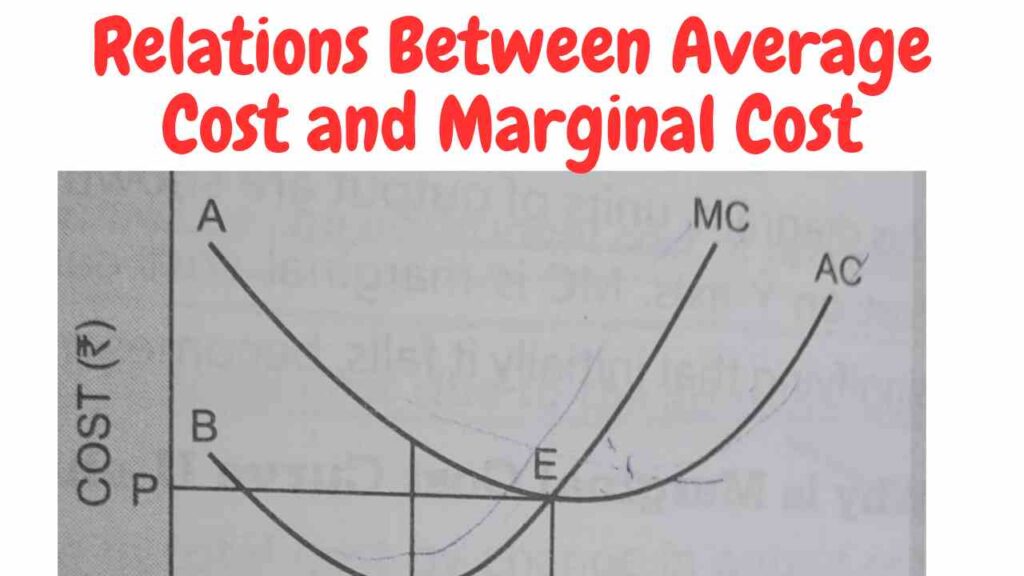
Relation Between Average Cost and Marginal Cost
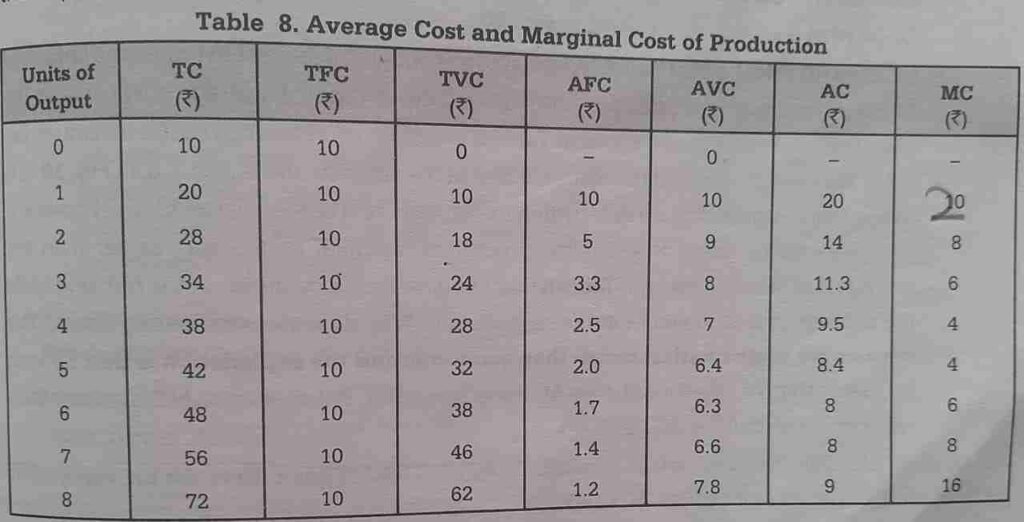
We can understand their relation between Average and Marginal Cost with the help of the following table. Let’s consider the following table for the purpose of a detailed relationship.
( 1 ) When AC Falls, MC is Less than AC:-
- When the AC curve is falling, the MC Curve will be below it.
- It is so because Whereas Average Cost is the aggregate of average fixed Cost ( AFC ) And Average Variable Cost ( AVC ),
- Marginal Cost refers only to Change in total variable Cost ( TVC ).
It can be understand with the help of following Figure
- The Rate of fall of the variable cost is faster than the rate of fall of both variable and Fixed Cost together.
- Beyond point F, additional total variable cost or MC tends to Rice, But the average of both fixed and variable Cost Continue to fall till point E on the AC Curve
- When both AC and MC become equal.
( 2 ) when AC Rises, MC is Greater than AC:-
- When Average Cost increased, Marginal Cost increased more than Average cost.
- But the rate of increase in marginal cost is more than of Average Cost.
- This is again because the rate at which additional Cost tends to rise is much faster than the rate at which Fixed Cost and Variable Cost together tend to increase.
From the following Figure we can understand as
- When Slope of the AC and MC Curve is upwards then MC Curve is above AC Curve as is Shown after point E in the Figure.
( 3 ) MC Cuts AC at its Lowest Point:-
- Marginal Cost is equal to Average Cost When the latter is at its Minimum.
- Above table shows that the average cost is minimum ₹8 at the seventh unit and the marginal Cost at the seventh unit is also ₹8.
From the following Figure we can understand
- It is Shown that the marginal cost Curve is Cutting the average Cost Curve at the latter’s lowest point E.
- It can be considered that the minimum point of marginal cost occurs earlier than the average Cost.
- From the table we see that marginal Cost is minimum at the fifth unit while the average Cost is Minimum at the seventh unit.
MC is less than AC, Then AC will be down towards it. But MC is greater than AC, then it will pull the AC Curve Up.
Conclusion:- MC is always to the left of AC and Cuts AC at its lowest point. Thus, the MC Curve must go through the bottom point of the AC Curve. Now we can understand the Relation Between Average Cost and Marginal Cost
Important Question of Economics
What are the different concepts related to costs? Explain the shape of the long run average cost curve according to traditional Theory. (2016 ) ( 2017 )
You can read love poetry on the way of study when you are tired on the way of study as per your interest.